Fixing Non-Manifold Meshes in Blender

One of the things that will make you fed up with Boolean modifiers in Blender is the non-manifold output. Unfortunately, there is no robust way to cover this issue. However, we can create a tool that can fix most (if not all) of the problematic meshes. This tool helps us fix non-manifold meshes in Blender.
Creating A Tool to fix Non-Manifold Meshes in Blender
In the photo below, you can see an example of a non-manifold result that appeared as a result of a Boolean difference of another cube from this one. If you apply another Boolean operation on this object, you will see that the object gets fully destroyed.
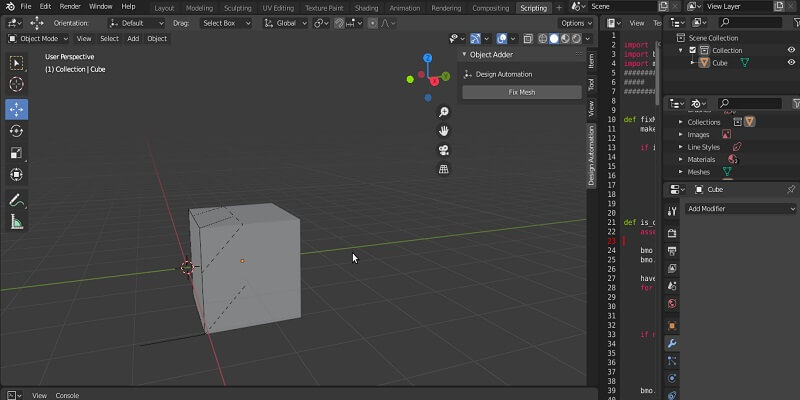
Python Scripts
In the scripts below we will get benefit from the functions that will eventually create a standard mesh that is the result of remeshing from triangular meshes to voxel-based meshes and also removing the non-manifold meshes.
import bpy
import bmesh
import math
####################################################################
##### Utility Functions
####################################################################
def fixMesh(obj_name):
make_voxel_remesh(get_object_by_name(obj_name), 0.5)
if is_object_have_non_manifolds(get_object_by_name(obj_name)):
print(obj_name, "have non manifolds")
if remove_object_non_manifold_loops(obj_name, loops=2):
print("Filled:", fill_non_manifolds(obj_name))
obj = get_object_by_name(obj_name)
make_smooth_remesh(obj, 9, 0.9, 1, True, True)
The above function is the main function for fixing the meshes. At first, it remeshes the object from triangular to voxel-based. Then, it will check whether has non-manifold parts and if the answer is yes, it will remove those parts. In the end, it will smooth and remesh the object.
def is_object_have_non_manifolds(obj):
assert obj.type == 'MESH', "Unsupported object type"
bmo = bmesh.new()
bmo.from_mesh(obj.data)
have = False
for edge in bmo.edges:
if not edge.is_manifold:
have = True
break
if not have:
for vert in bmo.verts:
if not vert.is_manifold:
have = True
break
bmo.free() # free and prevent further access
return have
The above function checks whether the object has non-manifold parts or not.
def deselect_objects():
bpy.ops.object.select_all(action='DESELECT')
def select_object_by_name(obj_name):
get_object_by_name(obj_name).select_set(True) # Blender 2.8x
def activate_object_by_name(obj_name):
bpy.context.view_layer.objects.active = get_object_by_name(obj_name)
def is_object_contain_selected_vertices(obj):
if obj.mode == "EDIT":
bm = bmesh.from_edit_mesh(obj.data)
else:
bm = bmesh.new()
bm.from_mesh(obj.data)
selected = False
for v in bm.verts:
if v.select:
selected = True
break
bm.free()
return selected
def remove_object_non_manifold_loops(obj_name, loops=0):
deselect_objects()
select_object_by_name(obj_name)
activate_object_by_name(obj_name)
removed = False
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode='EDIT')
bpy.ops.mesh.select_mode(type="VERT")
bpy.ops.mesh.select_non_manifold(extend=False)
if is_object_contain_selected_vertices(get_object_by_name(obj_name)):
if loops:
for i in range(loops):
bpy.ops.mesh.select_more()
bpy.ops.mesh.delete(type='FACE')
else:
bpy.ops.mesh.delete(type='VERT')
removed = True
bpy.ops.mesh.select_all(action='DESELECT')
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode='OBJECT')
return removed
def fill_non_manifolds(obj_name):
deselect_objects()
select_object_by_name(obj_name)
filled = False
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode='EDIT')
bpy.ops.mesh.select_mode(type="VERT")
bpy.ops.mesh.select_non_manifold(extend=False)
if is_object_contain_selected_vertices(get_object_by_name(obj_name)):
bpy.ops.mesh.fill(use_beauty=True)
bpy.ops.mesh.normals_make_consistent(inside=False)
bpy.ops.mesh.faces_shade_smooth()
filled = True
bpy.ops.mesh.select_all(action='DESELECT')
bpy.ops.object.mode_set(mode='OBJECT')
return filled
The above function will fill the open meshes.
def get_object_by_name(obj_name):
assert obj_name in bpy.data.objects, "Error getting object by name: {}".format(obj_name)
obj = bpy.data.objects
return obj
def make_voxel_remesh(obj, voxel_size, adaptivity=0, use_smooth_shade=True):
modifier = obj.modifiers.new(name='remesh', type='REMESH')
modifier.mode = 'VOXEL'
modifier.voxel_size = voxel_size
modifier.adaptivity = adaptivity
modifier.use_smooth_shade = use_smooth_shade
res = bpy.ops.object.modifier_apply({"object": obj}, apply_as='DATA', modifier=modifier.name)
assert "FINISHED" in res, "Error"
The above function will remesh the object to a voxel-based object.
def make_smooth_remesh(obj, octree_depth=9, scale=0.9, threshold=1, use_smooth_shade=True, use_remove_disconnected=True):
modifier = obj.modifiers.new(name='remesh', type='REMESH')
modifier.mode = 'SMOOTH'
modifier.use_smooth_shade = use_smooth_shade
modifier.octree_depth = octree_depth
modifier.scale = scale
modifier.use_remove_disconnected = use_remove_disconnected
modifier.threshold = threshold
res = bpy.ops.object.modifier_apply({"object": obj}, apply_as='DATA', modifier=modifier.name)
assert "FINISHED" in res, "Error"
####################################################################
######## Main Panel
####################################################################
class MainPanel(bpy.types.Panel):
bl_label = "Object Adder"
bl_idname = "VIEW_PT_MainPanel"
bl_space_type = 'VIEW_3D'
bl_region_type = 'UI'
bl_category = 'Design Automation'
def draw(self, context):
layout = self.layout
layout.scale_y = 1.2
row = layout.row()
row.label(text= "Design Automation", icon= 'OBJECT_ORIGIN')
row = layout.row()
row.operator("wm_function.myop", text= "Fix Mesh")
####################################################################
#### Main UI ّFunctions
####################################################################
class WM_Function_myOp(bpy.types.Operator):
"""Go to edit mode and determine the point then Click the button"""
bl_label = "Our customized function"
bl_idname = "wm_function.myop"
def execute(self, context):
fixMesh('Cube')
return {'FINISHED'}
def invoke(self, context, event):
return context.window_manager.invoke_props_dialog(self)
####################################################################
##### Register and Unregister
####################################################################
def register():
bpy.utils.register_class(MainPanel)
bpy.utils.register_class(WM_Function_myOp)
def unregister():
bpy.utils.unregister_class(MainPanel)
bpy.utils.unregister_class(WM_Function_myOp)
if __name__ == "__main__":
register()
Now if we run the code and click the Fix Mesh button in the panel, we will see that mesh of the cube has been fixed.
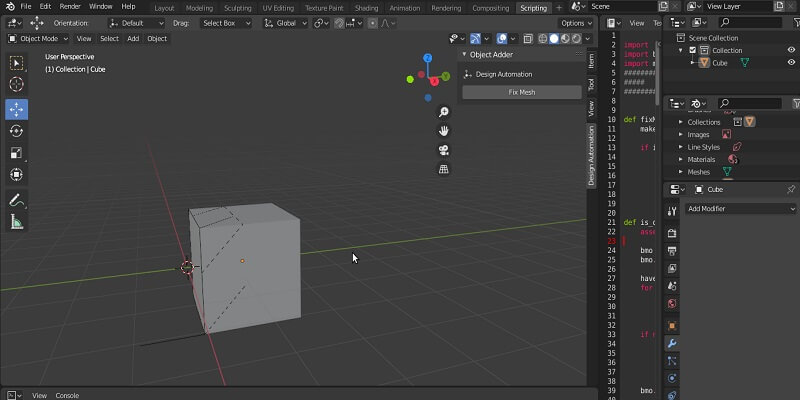
Fixing Non-Manifold Meshes: Done!
In this tutorial, we have managed to write the scripts of the utility functions that would help us remove or fix the non-manifold meshes in Blender. We have applied these utility functions in our main panel class and as a result, we have a fixed output.
Download this Article in PDF format

Check Out Our Services
In Arashtad, we're working on 3D games, metaverses, and other types of WebGL and 3D applications with our 3D web development team. However, our services are not limited to these. Back-end developments, front-end developments, 3d modeling, and animations are in our arsenal too.
See Our Services
Arashtad Serivces
Drop us a message and tell us about your ideas.
Tell Us What You Need
3D Development
https://blog.arashtad.com/3d/blender/fix-non-manifold-meshes-in-blender/
Comments
Post a Comment